imec
VUB
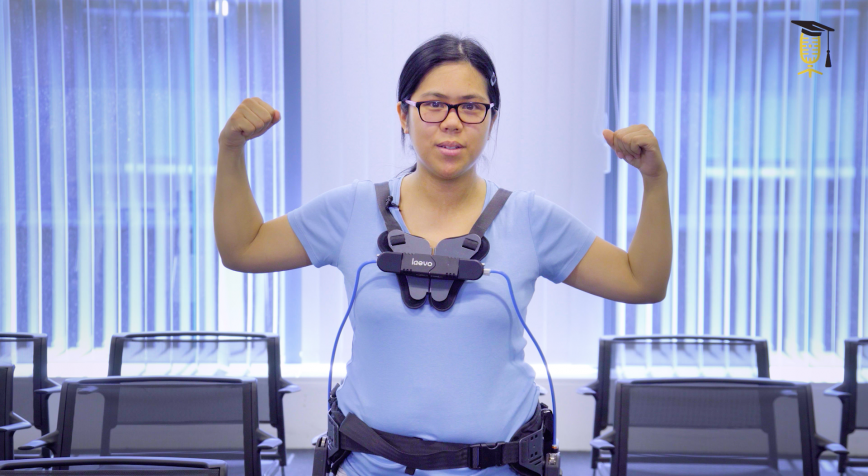
Will an exoskeleton give me superpower?
Industrial exoskeletons can support factory and construction workers in their heavy daily tasks and prevent back pain and other work-related injuries. So why exoskeletons not yet widely used in companies? That's what Shirley Elprama (Imec - VUB) is researching: she talks to companies and informs exoskeleton-designers so that they can build better exoskeletons in the future.