UHasselt
Is getting some fresh air always as healthy as we think?
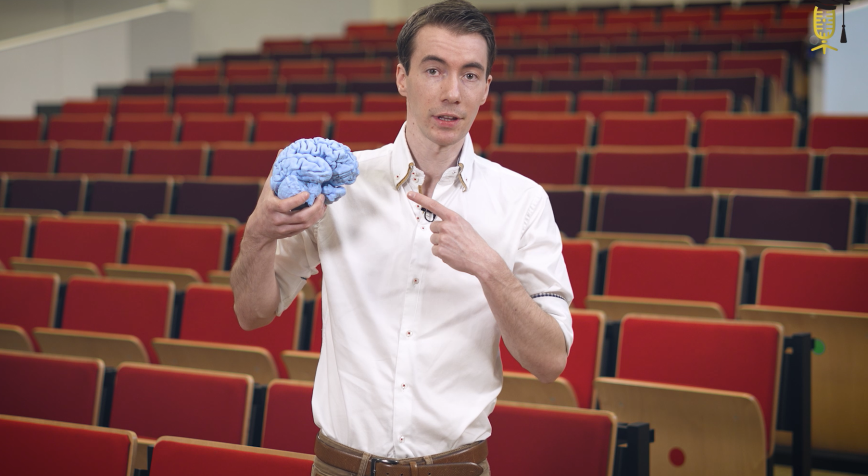
In the few minutes you watch this video, you breathe in thousands of fine dust particles. And did you know that this particulate matter can be found in your brain as early as 24 hours later? Biomedicist Kenneth Vanbrabant counts particulate matter particles in brain sections of deceased people. In this way, he wants to gather enough evidence so that governments can draw up better regulations for our air quality.