FWO
UGent
Smart cancer treatment of glioblastoma via networks
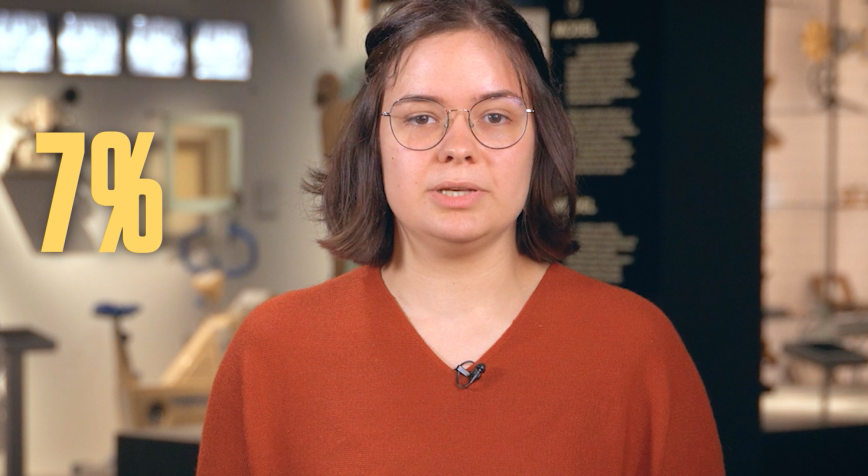
Today, we can treat cancer better than ever. Yet some cancer types remain very difficult to fight. Such is the case of glioblastoma, a highly aggressive brain cancer in which only 7 in 100 patients are still alive five years after diagnosis. Hoping to help glioblastoma get small, Joke Deschildre doctored a sophisticated strategy to attack cancer cells.