KU Leuven
Good characteristics of a malignant brain tumour
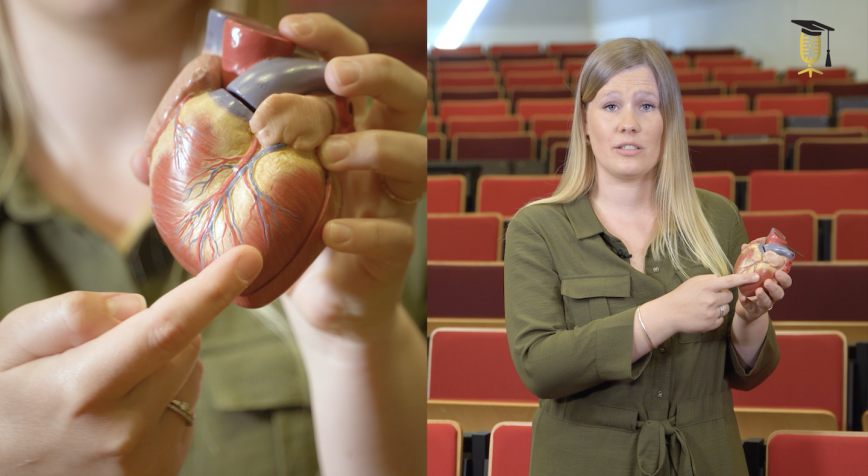
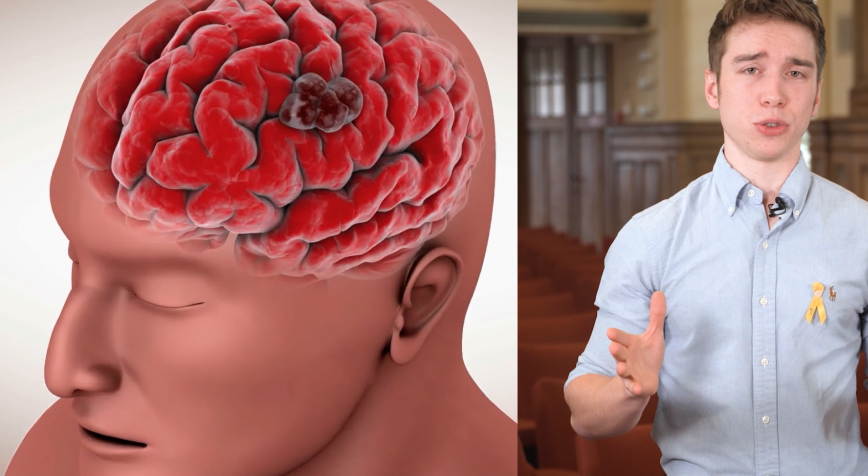
What if you only had 15 months to live? Hard to imagine, right? Yet every day, around 1,000 people worldwide hear this news. The verdict: glioblastoma, a malignant brain tumor. Yet a small group of patients manages to survive for more than 10 years with such a brain tumor. Brecht Decraene wants to finds out why.