FWO
KU Leuven
UGent
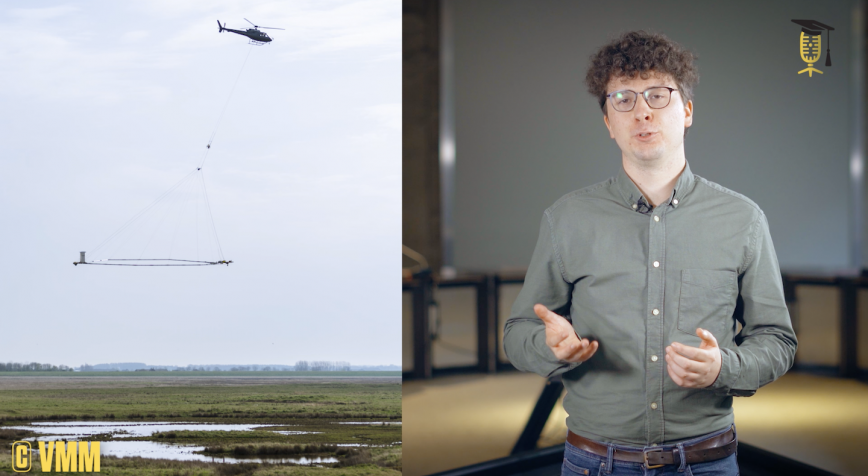
Mapping saltwater with a metal detector
Did you know that the sea can penetrate our lands and water resources unnoticed? Today, we find that saltwater in our polders, up to several kilometers inland. This salt water can make agricultural land and water supplies unusable. To find out exactly how far inland and how deep the saltwater problem reaches, Wouter Deleersnyder and his colleagues use a helicopter, a giant metal detector, and their knowledge of physics & geology. How all of this works, is explained by Wouter in this video.