KU Leuven
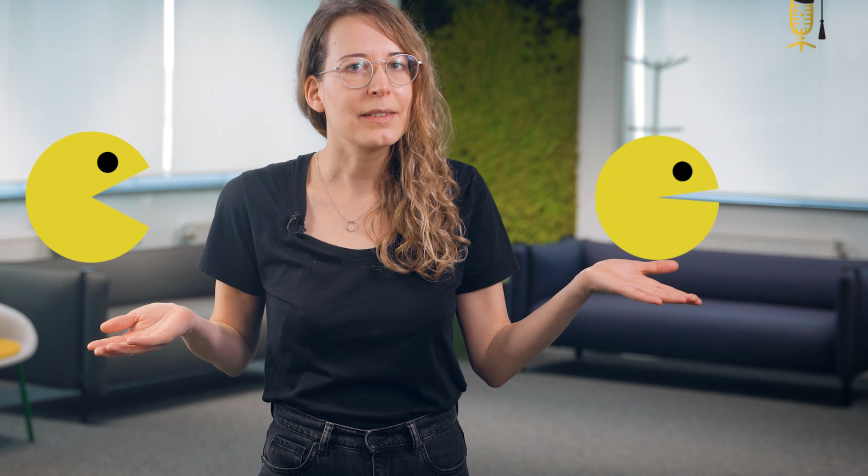
How to cure the Pac-Mans in our cells
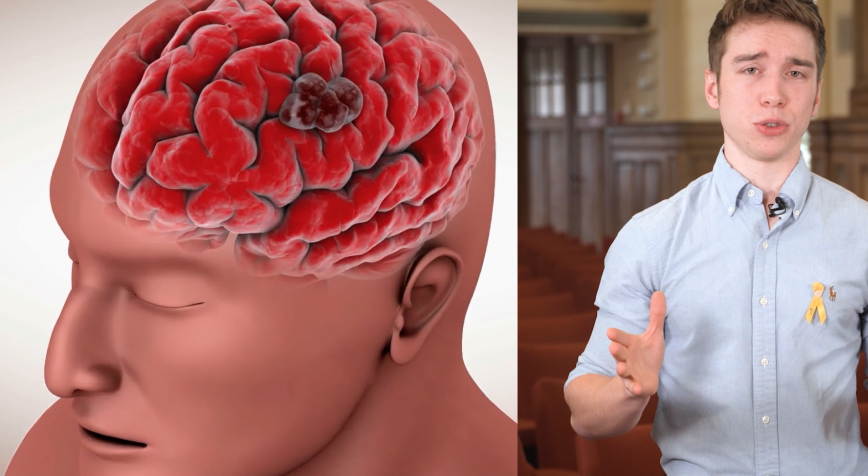
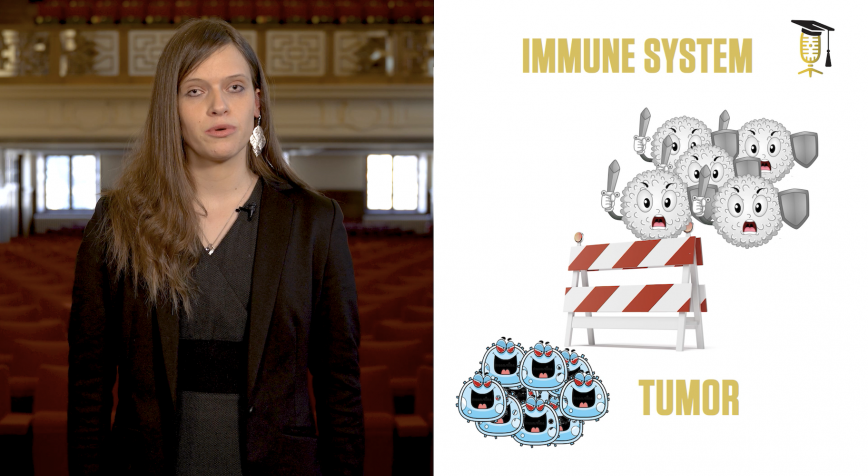
Do you remember Pac-Man, from that old skool computer game? Well, did you know that there are Pac-Mans in every single cell of our body? They're called enzymes. Some of these enzymes work too fast or too slow, and this can cause severe diseases. Michaela Prothiwa (KU Leuven) explains how she wants to track down these malfunctioning enzymes using a clever piece of chemistry.