FWO
KU Leuven
The AI that will help you sleep
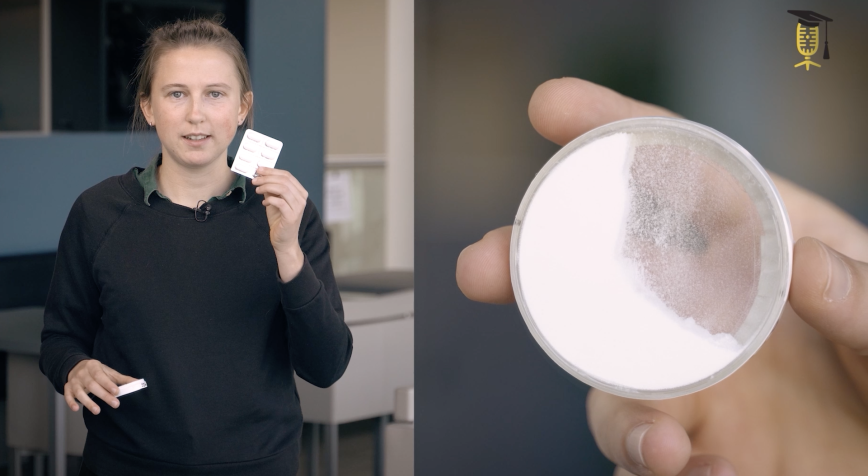
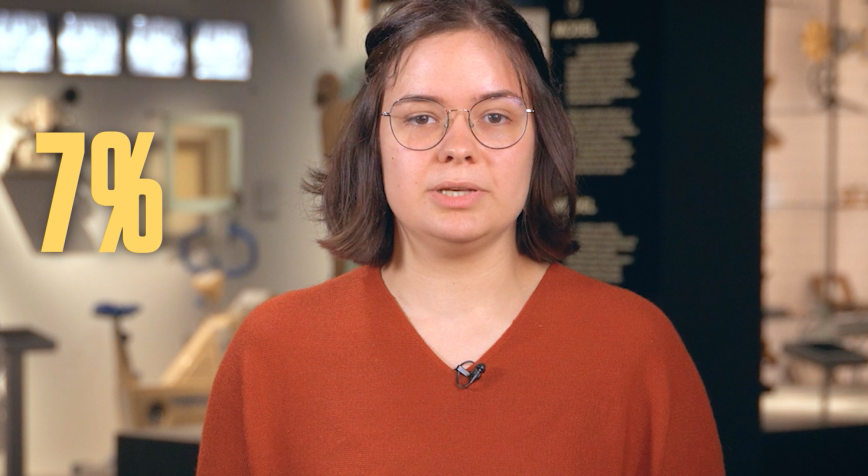
Do you ever wake up feeling like you have been run over by a truck? You are not alone. As many as 1 in 5 adults suffer from a sleep disorder, ranging from sleep apnoea to insomnia. With a compact, wearable device and AI, Elisabeth Heremans wants to analyse sleep problems in patients from the comfort of their own bed, instead of having them spend the night in a sleep clinic attached to a bunch of wires.