ILVO
KU Leuven
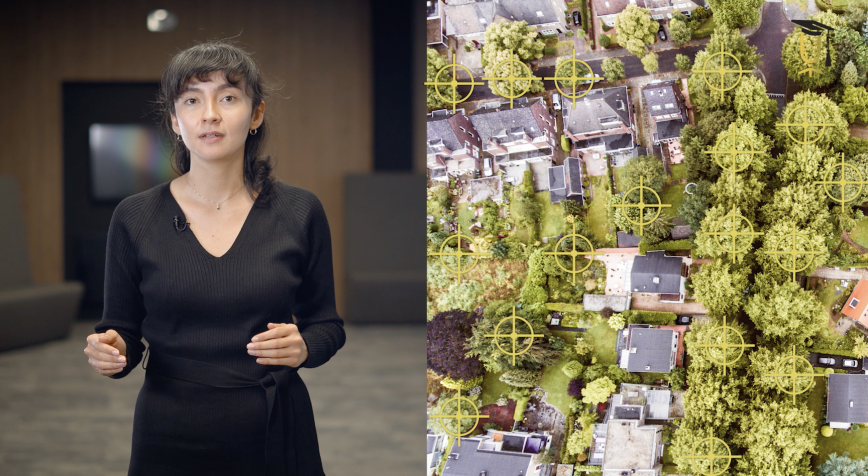
Drones map potato diseases
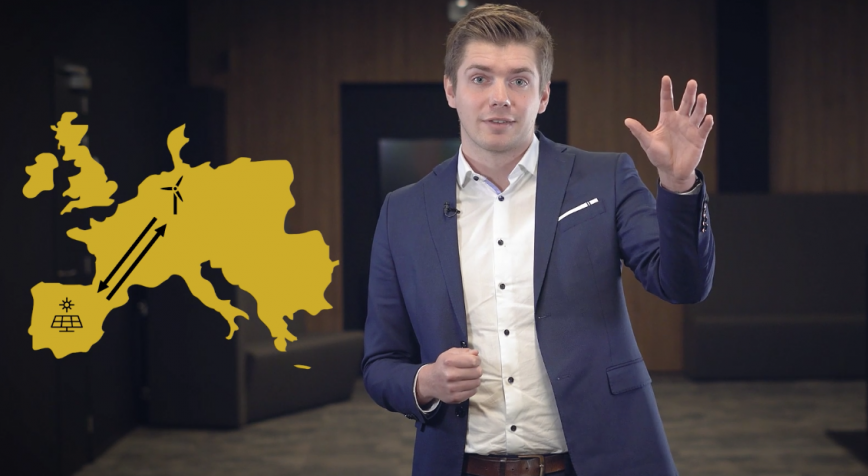
In Belgium, we grow a lot of potatoes. Unfortunately, potato plants are very susceptible to diseases. To prevent the spread of diseases, farmers spray their entire potato field with pesticides. Ruben Van De Vijver (ILVO) wants to use drones and artificial intelligence to spray only sick plants. Find out more in the video.